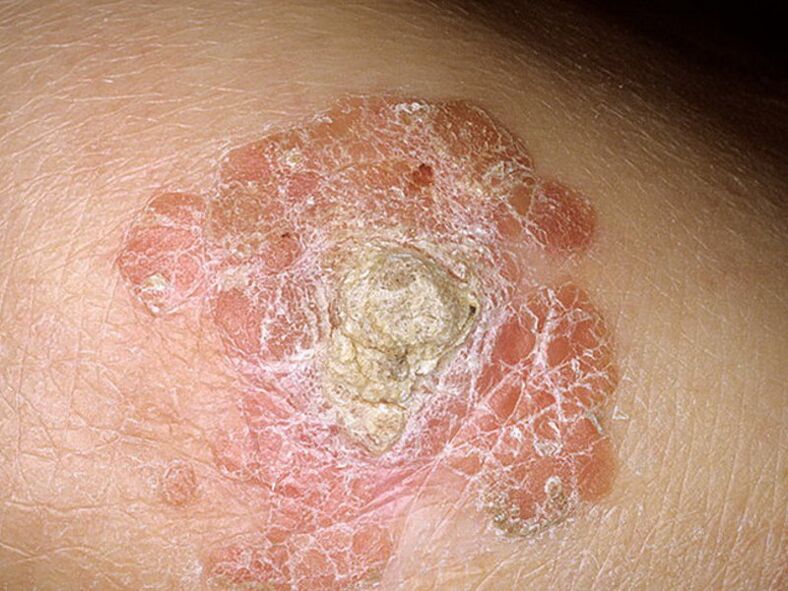
Papillomaviruses are a group of viruses of which there are approximately 24 subgroups. To date, about 600 species have been discovered. It only spreads from person to person. Many people and doctors face the problem of diagnosing and treating human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is capable of promoting tumor progression and is found in the skin, esophagus, oral mucosa, bronchi, conjunctiva and even the rectum.
Causes and routes of infection
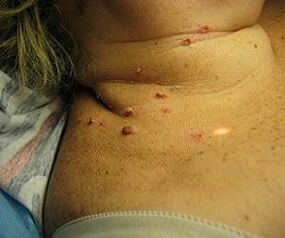
Human papillomavirus is a very common disease that is spread by:
- during sexual intercourse;
- to touch, to kiss;
- Scratches or cuts while going to a swimming pool, bathhouse, public restroom or gym;
- When shaving or depilating.
Statistics show that even with a partner, women are infected in 20% of cases.
About 70% of the population has the disease and is a carrier of HPV. The virus is especially active in the form of sharp or flat uneven growths on the skin and genitals from patients who have warts on their bodies (the very virus that causes them to appear). Medically, they are called warts and papillomas.
It is possible to infect the newborn from the mother during childbirth. In infants, the disease manifests in the form of throat or genital growths.
Symptoms and development of the virus
The incubation period (latency period) of the disease can last from two weeks to several years. Currently, there are no clear signs of the virus.
Warts on the skin can appear gradually, one at a time, but it's also possible for many condyloma acuminatum or papilloma to appear at the same time, similar in shape to sea cabbage.
HPV can manifest in women if the infection occurs through sex:
- in the labia area;
- vaginal;
- cervix;
For men:
- around the head of the penis;
- on the skin of the genitals.
When a partner is taken away by oral sex, the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat are affected, and for lovers of anal sex - the anus, the rectum.
Men rarely develop the disease, although they may be carriers of it. The virus is more common in women when examining spouses.
attention!If you notice a suspicious growth, see your doctor urgently, as some types of viruses can cause tumors to regrow, which can lead to cancer.
Classification and Type
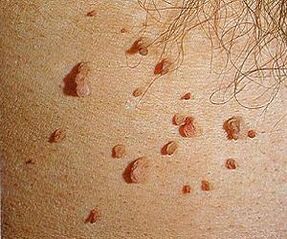
To date, about 600 viruses have been identified. They are mostly harmless and disappear within two years of infection with normal immunity.
However, about 40 species are dangerous to humans, causing benign and neoplastic tumors.
In the 1980s, doctors demonstrated the link between HPV infection and cervical cancer.
Depending on the location and variety of skin lesions, viruses can be divided into the following categories:
- sole;
- "Butcher's Wart";
- normal;
- flat.
On the genitals:
- genital warts;
- flattening, causing changes in the surface of the cervical membrane and causing oncology;
- Papillomas that cause cancer of the female and male reproductive organs and anus.
Other types:
- Oral mucosal damage;
- Respiratory papilloma;
- Tumors of the neck, head, lungs.
Variety:
- Simple papillomas appear on the back of the palms, and in children, they can grow on the knees. They look like conical, rough growths.
- Plantar - Interferes with walking, starts out as shiny growths, then grows into warts with rims on the bottom. Growing up, they formed a whole bunch of similar formations.
- Flat - The color is not much different from the skin, but can cause itching, redness, discomfort.
- Filamentous. Medically, they are called acrochords. They are more common in people over the age of 50. At first, they look like yellow bumps that are growing into growths up to 6mm long.
When warts appear in places that are visible to the naked eye, the patient can go to a medical institution. Determining failure of the cervix or vagina is more difficult, especially if the woman neglects to see a gynecologist.
virus diagnosis
You should definitely talk to your doctor if you have suspicious growths in the form of papillae (warts) or uneven, bumpy warts on your skin or mucous membranes. Warts don't cause cancer as often as flat papilloma, but it's best to remove them to reduce the chance of infecting those around them.
Such tumors are being studied due to the possibility of cancer development.
Doctors analyze for human papillomavirus - scraping from mucosal surfaces (colposcopy damage to the cervix - examining the mucosa under a strong magnifying glass) or skin. The samples are examined under a microscope for changes in tissue structure (dysplasia), as well as to determine the type of virus.
Based on the results of the cytology studies, cervical smears are divided into 5 categories:
- no change;
- Changes are caused by inflammatory processes;
- There are minor changes in cell structure, requiring histological examination;
- Cells with signs of malignant transformation are found;
- There are many cells with signs of cancer.
Histological examination can provide a more detailed understanding of changes in tissue structure.
The clinic uses a special HPV-test that allows you to get a more accurate analysis. A positive test result indicates that a malignant process is taking place in the tissue.
HPV has a high risk of cancer. The high risk of cancer is caused by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, which are present in 70% of cases examined.
Based on the test results, a diagnosis and a treatment plan are made.
HPV treatments
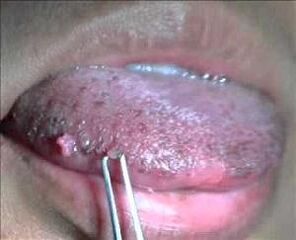
How is human papillomavirus treated? Regarding decreased immunity caused by disease, first, the doctor will prescribe drugs that increase immunity:
- Interferon;
- Interferon.
But the main treatment is the forced removal of the tumor by modern cosmetic methods:
- Diathermy electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction ("cauterize" with liquid nitrogen);
- laser removal;
- radio or chemical processing;
- Introducing an immunostimulatory or immunomodulatory agent into the growth.
In each disease situation, the type of treatment should be determined by a specialist.
If no cutaneous pathological process is found on the basis of examination results, only the papilloma of the surrounding small area of skin is excised. If malignant cells are detected, surgery can capture an important area, depending on the depth of the lesion.
Folk Methods and Recipes
How to cure human papillomavirus? Traditional medicine helps fight disease at all times. There is also considerable experience in the treatment of HPV.
Means recommended by traditional medicine. You can lubricate warts:
- celandine juice;
- Sour apple juice and its pomace;
- dandelion juice;
- ammonia.
Proven Recipe:
- Prepare Chaga, Celandine, String, freeze and use ice cubes 3-4 times a day.
- Lubricate with castor oil, then cover with a cloth. Usually 5-6 such programs are sufficient.
- Kerosene and walnuts. Grind unripe nuts in a meat grinder and blend: For 1 part nuts - 2 parts kerosene, the mixture should be infused for three weeks. Apply to warts 2 times a day.
In order to improve immunity, Chinese medicine practitioners recommend drinking
- potato juice,
- Echinacea Infusion,
- Rosehip tea.
Herbal Collection:
- Dandelion root, nettle, lemon balm, horsetail, plantain;
- Wormwood, St. John's wort, pansies, dill (seed), calamus (root), clover (flower), plantain.
Treating HPV at Home
You can remove papilloma at home with medicines sold in pharmacies:
- Special ingredients for frozen warts. It must be used with care so that it does not come into contact with healthy skin. After surgery, after about a week, the growths will disappear without leaving a trace.
- Treat with adhesive tape. It only takes 3 hours. But it can cause an unpleasant or painful feeling when ripped off.
- Dilute 2. 5 g of aspirin powder, equal parts iodine, 2 g of boric acid in 100 ml of alcohol and apply the composition to papilloma.
infection prevention
However, don't forget the viral nature of the unpleasant growth. Removing the papilloma from the surface of the skin makes it impossible to get rid of the disease. Therefore, you should see a specialist to prevent the tumor from degenerating into cancer. There is currently no complete cure for HPV, but you can take steps to avoid infection.
For prevention, you need:
- Use condoms for casual sex. A condom doesn't completely prevent HPV infection because it doesn't cover the entire surface of the skin to prevent contact, but it still partially helps prevent the infection from spreading.
- Avoid going to baths, swimming pools, toilets, even with the smallest wound on the skin.
- Children are vaccinated against cervical cancer, which is caused by the HPV virus. Girls aged 11-12 are vaccinated. Results from the vaccination showed that women who received the drug had fewer cases of the disease.
Have you found warts or suspicious growths on your body? Contact a competent expert and follow all advice. HPV can sometimes be very dangerous. Learn about treatment and removal and take action!














































































